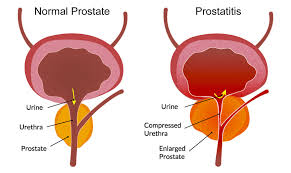
 Prostatitis is an infection that exclusively affects males. A male is diagnosed with acute prostatitis when his prostate gland becomes infected, leading to the organ’s inflammation. The prostate is a small gland that surrounds a man’s urethra, the tube that takes urine and semen out of the body. The prostate supplies nutrients to semen, performing an important role in reproduction. Description of causes, symptoms, and treatment of prostatitis are enumerated in the following paragraphs.
Prostatitis is an infection that exclusively affects males. A male is diagnosed with acute prostatitis when his prostate gland becomes infected, leading to the organ’s inflammation. The prostate is a small gland that surrounds a man’s urethra, the tube that takes urine and semen out of the body. The prostate supplies nutrients to semen, performing an important role in reproduction. Description of causes, symptoms, and treatment of prostatitis are enumerated in the following paragraphs.
Causes of Prostatitis
Below, we discuss the causes and symptoms of acute prostatitis, as well as possible complications and home remedies. A specific kind of bacterium which is responsible for causing STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) and urinary tract infections also causes prostatitis. Prostatitis is a common condition as approximately 50 percent of men are likely to experience it in their lifetimes. Acute prostatitis, on the other hand, is quite rare. Despite this, it is usually easy to diagnose because of some distinct characteristics.
Prostatitis Symptoms
An inflamed prostate gland exhibits symptoms that are somewhat similar to signs of a grave UTI. A weakened immune system and a clogged urethra are two fundamental causes of prostatitis. More often than not, acute prostatitis turns chronic or recurrent.
Common symptoms of Prostatitis include:
- fever
- pain in the pelvis
- blood in the urine
- chills
- pain above the pelvic bone
- pain in the rectum, testicles, or genitals
- increased frequency of urination
- pain during urination
- bad-smelling urine
- pain or discomfort during a bowel movement
- a weakened urine stream
- painful ejaculation
- blood in the semen
- trouble starting urination
- difficulty voiding the bladder
Treatment
 We at Fifth Avenue Urology normally treat prostatitis with antibiotics. We recommend our patients to continue taking the prescribed antibiotics for at least 4-6 weeks. The class of antibiotics that we stipulate to a specific patient depends on the type of bacterium responsible for the infection.
We at Fifth Avenue Urology normally treat prostatitis with antibiotics. We recommend our patients to continue taking the prescribed antibiotics for at least 4-6 weeks. The class of antibiotics that we stipulate to a specific patient depends on the type of bacterium responsible for the infection.
Sometimes, we prescribe medicines that work towards easing acute prostatitis’ symptoms. For instance, we advise the patients to take OTC (over-the-counter) anti-inflammatory medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for getting relief from pain. We also suggest alpha-blockers that function as effective muscle relaxants, enabling the prostate’s and bladder’s muscle fibers to relax.
A relaxed prostate gland and urinary bladder enable a patient to release urine from the latter more comfortably. We only recommend hospitalization to a patient when antibiotics, beta-blockers, or anti-inflammatory medications do not help relieve acute prostatitis’ symptoms. A high dosage of antibiotics may have to be administered intravenously for the entire period of hospital stay.
We usually suggest patients try some home remedies besides taking medicines. For instance, we tell them to drink plenty of water, avoid alcohol, stay away from spicy foods, and so on. We tell patients to make a few lifestyle changes to minimize the risks of chronic or acute prostatitis.
Some of the changes include taking a balanced diet, alleviating stress, staying fit and trim, using contraceptives during intercourse, and so on.
Conclusion
Our urologists strongly believe that majority of acute prostatitis cases can be treated effectively with antibiotics. Nevertheless, some patients may need to stay in a hospital for a short duration. There’s every possibility of an acute form of the condition turning chronic.
The patient may have to make lifestyle changes for alleviating chronic prostatitis symptoms. Those diagnosed with chronic or acute prostatitis can contact our urologists at Fifth Avenue Urology for an appointment and detailed consultation.
